What Best Describes the Basic Way in Which Soils Form
3 What are the 5 ways soil is formed. Soil aggregates are a fundamental concept in soil.
1 the top layer of earth 2 vegetation grows on the loose surface of earth.

. For a soil to be healthy it must have good structure. SANDY CLAY and LIGHT CLAY Will form ribbon 50 75 mm soil ball is plastic consistency like putty with slight resistance to shearing. What best describes the basic way in which soils form.
4 What are the 4 steps of soil formation. Which of the following describes a way in which soil is formed. Like a biography each profile tells a story about the life of a soil.
Deposition is the accumulation of new materials that have been eroded from another place such as river gravels or blown gravel or. The process of soil formation is through the rock cycle together with the integration of soil microbial and chemical activities originating from living organisms. These layers are known as soil horizons.
Soil is made up of a combination of primary particles sand silt and clay. 7 How is soil formed Class 7. 8 What is soil formation in agriculture.
6 How is soil formed Class 5 answer. Cold temperatures freeze the surface of a pond. The soil formation process depends upon the presence of new soil material which is either acquired by denudation or deposition.
Soil consists of a solid phase of minerals and organic matter the soil matrix as well as a porous phase that holds gases the soil atmosphere and water the soil solution. What best describes the basic way in which soils form. Big rocks break down into smaller rocks by continuous action of wind and rain.
The depth of different horizons can be very important to understand a soils characteristics. When they are all combined these horizons or layers form the soil profile. In fall leaves change colors from green to orange.
They form pores that help soils retain water and air. They are produced from rocks parent material through the processes of weathering and natural erosion. Soil properties such as soil colour or texture and is defined by an upper and lower depth.
An aggregate formed in the soil and may be an aggregation of smaller peds and is. Over time more distinct soil horizons will. 5 How is soil formed short answer 2.
What best describes the basic way in which soil forms. 2 How is soil formed simple answer. Which of the following best describes soil texture.
For instance during the decomposition of dead plants and animals nutrients are mixed up with the weathered and disintegrated rocks to form soil. 2 3 Accordingly soil scientists can envisage soils as a three- state system of solids liquids and gases. Submerged rock that is not stable or.
Material in a sloped layered system where the layers dip into the excavation or a slope of. These particles can be bound together into what soil scientists call aggregates Soil aggregates retained on a 475 mm sieve after wet sieving experiment. What describes how topsoil or A-horizons develop.
A soil profile is a vertical cross-section of the soil made of layers running parallel to the surface. Physical and chemical weathering of rock Shoreline retreat is a natural process that humans have made worse in recent. Water wind temperature change gravity chemical interaction living organisms and pressure differences all help break down parent material.
Put the horizons together and they form a soil profile. Has a wide variety of soils and each this US. The improvement of soil quality by fertilizers.
Within a few years of starting conservation practices such as implementing. Many plants cannot grow in sandy soil. Soil minerals form the basis of soil.
The proportion of sand silt and clay particles. Generally soil refers to. Sandy horizon with upper depth.
9 How do soils form quizlet. Soils form typically at 1 m depth from surface. Hot temperatures heat the surface of a pond.
- separated from other similar aggregates by an obvious pattern of cracks or partings or- has distinct surfaces over at least one-half of the aggregate. Soil has a story to tell us about of its origin. Submerged soil or soil from which water is freely seeping.
It takes many years for these rocks to break down into smaller rocks. Granular soils including gravel sand and loamy sand. A a cold dry climate B a cold wet climate C a hot dry climate D a hot.
The breakdown of soil by chemicals. On a rainy day water washes small particles of rock off of a large rock. Soil Changes with Age - As a soil ages it gradually starts to look different from its parent material.
Which of the following best describes soil erosion. The movement of soil by wind or water. The soil is arranged in layers or horizons during its formation.
Rocks are mainly broken by two types of weathering- physical weathering and chemical weathering. Accumulation of organic matter in the upper topsoil. 3 all terrestrial life depends on soil.
Or- has coatings over at. 1 Describe How Soil Forms. The proportion of sand silt and clay particles.
Physical and chemical weathering of rock. The soil is the topmost layer of the earths crust mainly composed of organic minerals and rock particles that support life. In sandy clay you can see feel and hear sand grains whereas light clay is smooth to.
Denudation is the abrasion of present rock material by the action of ice water or wind. The breakdown of soil by drought. Aggregates are groups of soil particles that bind to each other more strongly than to other particles.
Thats because soil is dynamic. Soil aggregates can change quickly. 10 How are soil formed Class 10.
For example a soil with a. Soil formation takes place in the following ways. CLAY LOAM Will form ribbon 40 50 mm soil ball holds together strongly and is plastic consistency like putty and smooth to manipulate.
Soil Profiles - Dig down deep into any soil and youll see that it is made of layers or horizons. In what type of climate would soil form fastest from limestone bedrock. How do soils form.

Preparing And Improving Garden Soil Usu
Why Is Loam Important To Agriculture Quora

Cabot Ct1 Paprika Paprika 2 X3 In 2021 Dalyn Stylish Rugs Rugs

Soils Soil Horizons Apes Ch 8 Weathering Of Minerals Ppt Download

To Obtain A Good Soil Sample For Testing Follow These Simple Steps From Agsource Laboratories Http Soil Testing Agriculture Education Gardening Infographic
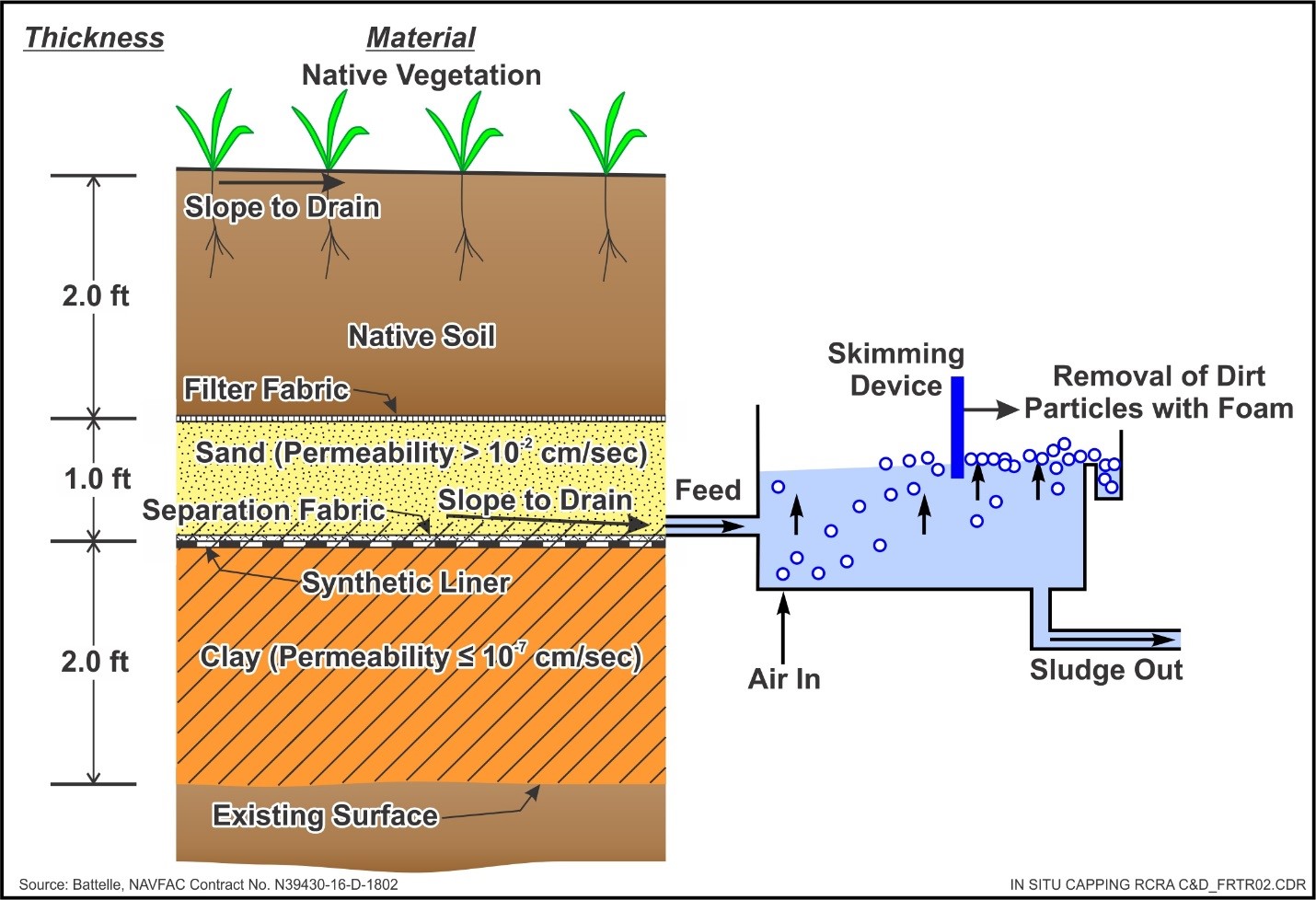
Landfill And Soil Capping Frtr Remediation Technologies Screening Matrix
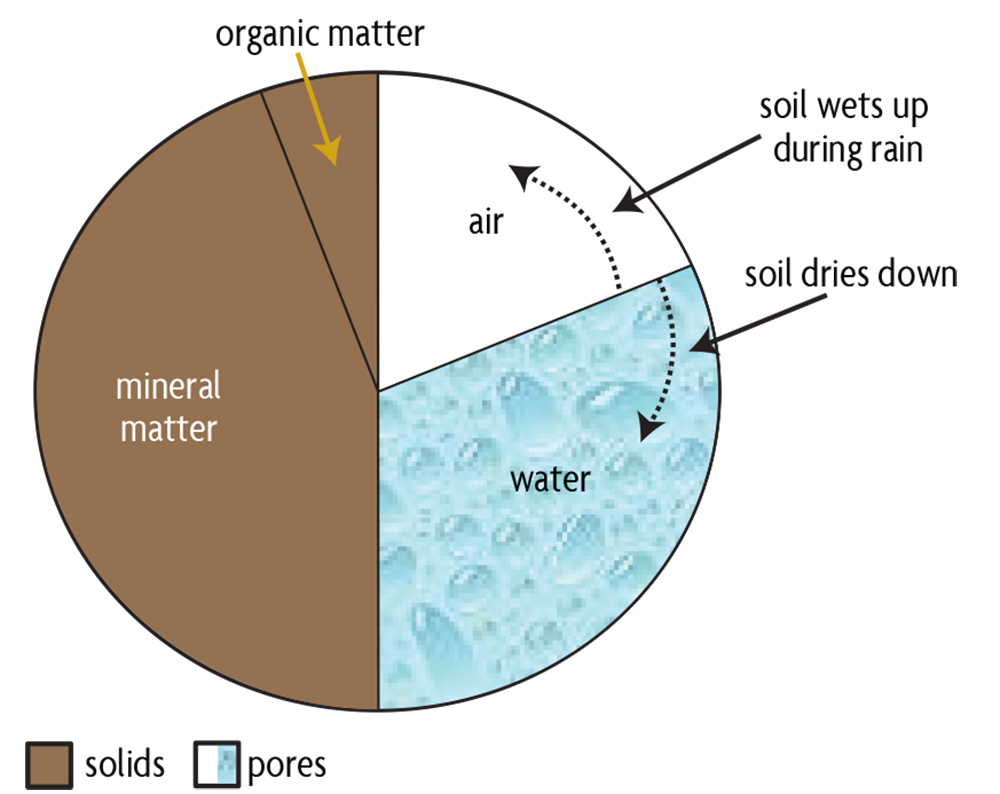
Ch 5 Soil Particles Water And Air Sare

Soil Genesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Pin By Taylor Vanderyagt On Soil Soil Texture Plant Science Soil

Soil Basics Soil Science Society Of America

Soil Basics Soil Science Society Of America

Soil Profiles And Types Geology
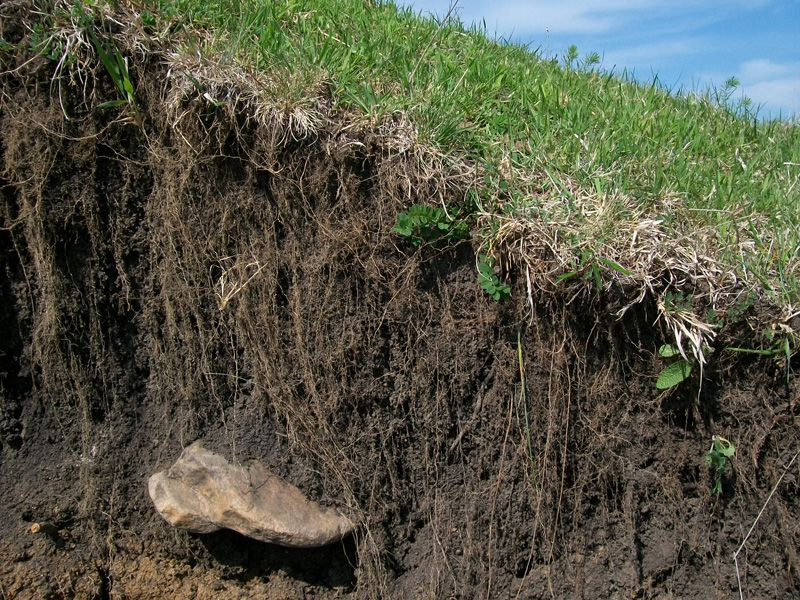

Soil Basics Soil Science Society Of America

Soils Soil Horizons Apes Ch 8 Weathering Of Minerals Ppt Download




Comments
Post a Comment